A Cutting-Edge Delivery System Dramatically Enhances Bioavailability of Glutathione and Other Nutrients

- An Impressive New Delivery System For Nutrients |
- Overcoming Glutathione’s Poor Absorption |
- Results of Preclinical Studies |
- The Unique Characteristics of Whey Protein as a Nutrient Delivery System |
- Glutathione with Provail® in Clinical Settings |
- Why Microencapsulation? |
- Microencapsulation Improves Other Nutrients’ Bioavailability |
- Promising Future Applications of Encapsulation with Whey Protein |
- Conclusions
INTRODUCTION
Poor absorption and nutrient instability have plagued the nutritional medicine field and have limited the clinical efficacy of many highly promising nutrients. Patients must take large and sometimes unrealistic amounts in order to obtain any effect. Certain nutrients cannot survive the harsh environment of the gut or they may break down easily at room temperature or with sunlight exposure. Other nutrients may have reduced bioavailability; they may not readily absorb in the gastrointestinal tract without a fatty meal to accompany them, for example. Bioavailability describes how well a nutrient is absorbed and utilized.1 There have been a number of delivery systems introduced to overcome these obstacles with varying success.
The question is how do we protect nutrients and enhance absorption so that we can effectively deliver them to tissues and achieve better clinical results? The solution is a revolutionary delivery system that has been applied effectively to enhance stability and absorption of many nutrients including diindolylmethane (DIM), quercetin, and probiotics.2,3 When this technology was applied to glutathione, the results were remarkable.
DaVinci Laboratories is ushering in this bioavailability-boosting technology through Glutathione with Provail®, a highly stable, absorbable, and biologically active oral form of glutathione. Backed by scientific studies, Glutathione with Provail® will likely become the best glutathione supplement on the market by setting the benchmark for glutathione bioavailability. Throughout this paper, Glutathione with Provail® is interchangeably referred to as whey protein encapsulated glutathione, whey encapsulated glutathione (WEG), glutathione encapsulated in polymerized whey protein (PWPC-GSH), or whey protein matrix. DaVinci Laboratories also is introducing Glutathione Bright with Provail®, a skin-support supplement that uses the same whey protein encapsulation technology.*
DON'T HAVE TIME TO READ THE ENTIRE WHITE PAPER NOW?
Fill out the form and download a PDF version of the guide you can reference later.
An Impressive new delivery system for nutrients

DaVinci Laboratories has introduced a novel nutrient delivery system developed by a leading scientist. This delivery system is a new patented technology and uses a state-of-the-art processing technique. Here’s how it works: Whey protein is put through a series of physio-chemical reactions which result in beneficial structural changes.2 These structural changes transform the whey proteins into a matrix of ultra-small particles, 150-300 nanometers in diameter. Similar in size to casein micelles (protein and mineral clusters) in milk, this new polymerized whey protein matrix coats the nutrient to protect it from degradation and enhance absorption. Think of the polymerized whey protein (PWP) as an envelope that contains a nutrient inside of it. Later in the digestive tract, the envelope will open and release the nutrient for absorption.
Whey protein encapsulation provides many benefits:
- Enhances absorption of an unstable nutrient or one with a poor bioavailability profile*
- Protects it from degradation in the stomach*
- Improves delivery of the nutrient
- Increases the nutrient’s clinical efficacy*
- Extends the nutrient’s stability by resisting degradation and oxidation*
The unique attributes of whey protein complement this nutrient delivery system and are discussed later in “The Unique Characteristics of Whey Protein as a Nutrient Delivery System” (page 4).
Overcoming Glutathione’s Poor Absorption
Whey encapsulated glutathione holds potential for any number of nutrients that are difficult to absorb. However, DaVinci Laboratories first applied this raw material delivery system to glutathione given its tremendous breadth of clinical applications and notoriously poor bioavailability.2
Glutathione (gamma-glutamyl-cysteinyl-glycine), the “master antioxidant,” is present in almost every cell of the body and is rich in thiol (-SH) groups. It is a tripeptide comprised of three amino acids: cysteine, glutamic acid, and glycine. Glutathione in its reduced form scavenges free radicals. Oxidized glutathione is “used up” glutathione, which must be continually recycled to satisfy the antioxidant needs of the cell. Optimal glutathione levels are necessary for immune system function,4 phase II detoxification,5 blood sugar metabolism,6 and heart,2 joint,7 and neurological health.*6,8
Unfortunately, GSH is easily broken down in the intestinal tract and liver and only small quantities reach circulation.9 Storage stability of glutathione is also poor. When it is exposed to heat and light, its antioxidant activity is reduced.2 There is ongoing debate as to whether orally administered GSH is absorbed because it failed to raise plasma glutathione levels in some studies. Additionally, there is no specific carrier of GSH at the cell membrane level.10 Consequently, many clinicians have avoided the direct use of GSH supplements and instead focused on GSH precursors, such as N-acetylcysteine, to boost endogenous production.*11 However, in 2015, a clinical study of pure powdered glutathione increased erythrocyte, plasma, and lymphocyte glutathione levels after six months of use in humans, suggesting that some is absorbed after all.*12
Finally, an oral glutathione that increases blood levels 2.5 times more than other forms.
How Whey Protein Encapsulated Glutathione Raises Blood and Tissue Levels
Whey encapsulated glutathione proved to be an effective and powerful way to enhance the bioavailability and stability of GSH.* Whey encapsulated GSH created a matrix that led to improved absorption of glutathione.* GSH was effectively delivered to tissues throughout the body. The study authors suggested that whey encapsulated GSH was better shielded from stomach acid and the digestion by pepsin in the gastrointestinal tract13 and thus better absorbed.* Whey encapsulated glutathione produced a high surface charge that made the product highly stable and improved absorption.* Finally, whey protein is rich in substrates, which further supported endogenous production of GSH.14,15

Results of Preclinical Studies
Whey protein encapsulated GSH improved bioavailability and antioxidant capacity in animal models.* A 2021 animal study published in Molecules by Zhang and colleagues investigated both the bioavailability and safety of whey encapsulated GSH.2 Rodents were given a saline control, polymerized whey protein concentrate alone, 100 mg/kg of GSH in a pure (98.7%) powder form, or 100 mg/kg GSH encapsulated with whey protein concentrate (Glutathione with Provail®).2 Note that the pure GSH powder used in this study is that of a leading competitor . Plasma glutathione levels were measured after oral administration at 0, 15 min, 30 min, 1 h, 2 h, and 4 h in each group of six mice.
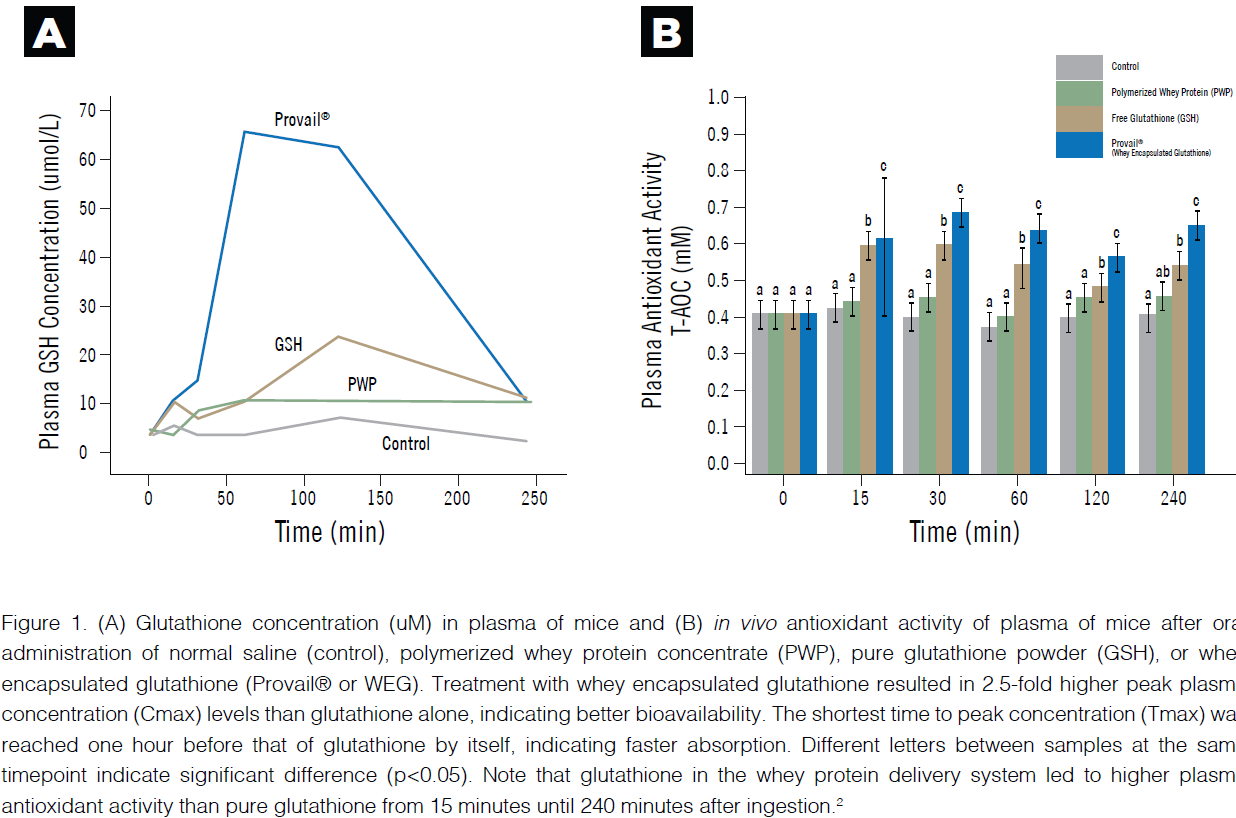
Faster and better absorption*
Compared to free GSH, there was a 2.5-fold higher maximum plasma GSH concentration in animals who were treated with whey encapsulated GSH. There was 2.6-fold increase area under the curve. These findings showed significantly increased bioavailability of GSH in the whey protein delivery system when compared to pure isolated GSH. Further, animals given the GSH in a whey protein matrix re ached maximum plasma content ration in only an hour compared to two hours for free GSH. These results show effective and fast absorption of WEG.*

Improved antioxidant activity*
Beyond plasma levels that showed fast and effective absorption, a functional assessment of glutathione activity confirmed biological effects of glutathione. Compared to mice given free GSH, whey encapsulated GSH resulted in significantly increased antioxidant capacity in the plasma through the entire period of study (from 15 minutes until 240 minutes after ingestion).*
Non-toxic
In the 28-day toxicology arm of the study, a diet containing up to 4% GSH in a whey protein matrix was found to be safe and non-toxic. According to the study authors, “Data indicated that polymerized whey protein concentrate may be an effective carrier for GSH to improve bioavailability and antioxidant capacity.”* 
Zhang and colleagues’ additional (to date unpublished) findings showed that three to four hours after rats were fed whey encapsulated GSH, GSH levels in the brain and liver tissues were significantly higher compared with rats fed free GSH. 16 This provides compelling preliminary findings that in addition to elevating plasma levels, whey encapsulated GSH may reach target organs such as the liver and may effectively cross the blood-brain barrier.

The Unique Characteristics of Whey Protein as a Nutrient Delivery System
Whey protein serves as an excellent delivery system due to its ability to carry hydrophobic compounds such as polyphenols and fat-soluble substances such as oil and vitamins.2,17,18 Previous research has demonstrated its effectiveness as a delivery system for astaxanthin, diindolylmethane (DIM), quercetin, vitamin D, and probiotics.2,19-22
Whey protein itself is associated with numerous health benefits.* Whey protein is derived from cows’ milk and is a co-product of the cheese-making process. It is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) and is highly nutritious with a complete amino acid profile. Whey has abundant cysteine residues which could support the in vivo production of glutathione or phase II sulfation.* It is rich in beta-lactoglobulin and alpha-lactalbumin, two immune-enhancing proteins that can act as prebiotics, promote tissue repair, maintain intestinal integrity, inhibit pathogens, and eliminate harmful substances.*23,24 Furthermore, whey protein is an antioxidant,24,25 maintains healthy and flexible arteries,26 and may support some aspects of cognitive function.*26 It also enhances muscle strength.*27,28
Polymerized whey protein has unique particle structural characteristics compared to other proteins. Its functional properties make it ideal for carrying nutrients (for example, it mixes well with other molecules and doesn’t separate).3 In addition, with polymerized whey protein, there are no additional chemicals used in the production process. It is free of solvents and polysorbates. Glutathione with Provail® therefore contains only glutathione and whey protein and the minimal ingredients required to manufacture the capsules.
Glutathione with Provail® in Clinical Settings
Davinci Laboratories’ Glutathione with Provail® and Glutathione Bright with Provail® are exceptional replacements for poorly absorbed oral glutathione formulas. These novel, patented encapsulations of glutathione are more stable, increase plasma levels 2.5 more times than pure glutathione, and more effectively increase antioxidant capacity.* The whey protein used in DaVinci Laboratories’ Glutathione with Provail® and Glutathione Bright with Provail® does not contain hormones or gluten and is free of genetically modified organisms. It is free of solvents and polysorbates. That’s because whey encapsulated GSH requires no additional chemicals in the production process.
Glutathione with Provail® and Glutathione Bright with Provail® Health Benefits Include:
- Improved mood, memory, and cognition*

- Counterbalance to conditions of oxidant stress*
- Detoxification support*
- Healthy immune function*
- Tissue regeneration/rehabilitation*
- Antioxidant activity*
- Skin health*
A pure form of glutathione- the leader in the market- was used in the Zhang et. al. study as the positive control. A 2015 clinical study showed that it increased erythrocyte, plasma, and lymphocyte glutathione by 30 -35% after six months of use in humans. It also reduced oxidative stress and increased natural killer cytotoxicity, testifying to its arrival and bioactivity at the tissue level.* When compared head-to-head, Glutathione with Provail® had better bioavailability and faster absorption in this animal model.2 Plasma concentrations of glutathione were 2.5 times greater in the Glutathione with Provail® group compared to the pure form of glutathione group and peaked more quickly.2 Glutathione with Provail® increased antioxidant activity more than the pure glutathione at every timepoint.2 This shows promise for the superior bioavailability and clinical efficacy of Glutathione with Provail®.
Why Microencapsulation?
Clinicians want high-quality, effective dietary supplements. However, manufacturers struggle to effectively package and deliver fragile bioactive nutrients. Examples are vitamin C, fish oil,
probiotics, and iron. Nutritional ingredients might break down in heat or moisture. They might be too sticky to process efficiently. They might taste or smell bad. Or they might not work as intended because they aren’t bioavailable or because they interact with other dietary factors.
Manufacturers try to overcome these limitations by adding excipients. They might overshoot the dose on the label, anticipating the loss in stability while in storage. Manufacturers have tried to enhance absorption of fat-soluble nutrients, using microemulsions, microcapsules, liposomes, and micelle-forming compounds.29
Microencapsulation has emerged as an exceptional solution to the challenges of packaging and delivering inherently sensitive natural ingredients.30 Microencapsulation has a long history of use in the pharmaceutical, nutrition, and food science fields. As described earlier, the process takes tiny bioactive substances and protects them from their environment by enveloping them within a protective barrier coating material.30 Manufacturers have used various substances to provide this protective barrier—usually some type of starch, gelatin or lipid matrix that is combined with several other excipients, chemicals, or it may require substantial processing like hydrogenation.
Whey protein encapsulation offers a new unique solution. It effectively surrounds a nutrient in an envelope and protects it through its journey in the digestive tract until digestive proteinases “open” the whey envelope and release the nutrient for absorption. It requires no excipients and minimal chemical processing, yet still provides a protective barrier and a vehicle to deliver nutrients and improve bioavailability. The result is a cleaner process and a healthier end product.
Whey Protein Encapsulated Glutathione vs. Liposomal Glutathione
Various glutathione supplements have been developed to overcome the challenge of its poor bioavailability. One example is liposomal glutathione; marketed as a more absorbable form of glutathione. Liposomes are hollow spheres, composed of phospholipids, that can be filled with nutrients. Liposomes enhance absorption of nutrients in the GI tract and protect the nutrient from breakdown.
Liposomal glutathione contains carriers and additional inactive ingredients. The whey-protein encapsulation method used to make Glutathione with Provail® does not require any of these other carriers. It is free of inactive ingredients that would affect its absorption and quality. It is therefore a simpler and purer glutathione supplement than many liposomal forms.
Liposomal GSH products use fat as their main ingredient to encapsulate the glutathione. Glutathione with Provail® and Glutathione Bright with Provail® use only protein in the form of whey protein to encapsulate the glutathione. This is beneficial because the whey protein has added nutritional properties that a lipid encapsulation system does not have.* It promotes tissue repair, strengthens the intestines, detoxifies the body, and synergistically works together with glutathione to raise levels of this important antioxidant.*
Microencapsulation Improves Other Nutrients’ Bioavailability
In addition to GSH, whey protein encapsulation has a proven track record of success with other nutrients that suffer from low-bioavailability or breakdown during storage. For example, 3,3’-Diindolylmethane (DIM) is sensitive to light during storage, and has limited solubility in water and physicochemical instability.3 In an in vitro study, whey protein encapsulated DIM particles enhanced DIM photochemical and pH stability when compared with native DIM.3 This new delivery system makes nutrients more stable and resistant to degradation from UV light or other stresses. In addition, DIM by itself is an irregular shape. However, when enclosed inside a whey protein matrix, the edges of the DIM molecules are smoother which improved bioavailability. This indicates whey encapsulated DIM has excellent bioavailability and enhanced effectiveness.
Lactobacillus plantarum probiotics encapsulated with whey were better protected from the harsh conditions of the digestive system. These probiotics adhered to the whey protein, resulting in Lactobacillus becoming embedded within the walls formed by the protein.20 Furthermore, research conducted using the carotenoid astaxanthin also led to promising results. Astaxanthin has poor water solubility, a high melting point, low bioavailability, and is vulnerable to chemical breakdown under conditions such as an acidic environment and exposure to heat, light, and oxygen.19 In a cell culture model of intestinal absorption, whey protein encapsulation was found to increase bioavailability of astaxanthin by 16.1 times, likely due to a decrease in particle size caused by the whey protein delivery system.19 The researchers concluded that the bioavailability of astaxanthin could be significantly improved by whey protein-based encapsulation.
These studies demonstrate exciting potential for the use of polymerized whey protein technology to:
- Improve the stability of the nutrient*
- Keep nutrients intact in the GI system*
- Decrease particle size for better absorption*
- Enhance nutrient blood levels and delivery to tissues*
- Improve the clinical effectiveness of a supplement*
Promising Future Applications of Encapsulation with Whey Protein
Although DaVinci Laboratories has chosen to introduce this technology with GSH, there are limitless possibilities for its use. For example, coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is a fat-soluble dietary supplement that is best absorbed with high-fat meals. It is a huge molecule that is difficult for the body to absorb because it can only pass through the intestine by passive diffusion.31,32 Using a whey protein delivery system with CoQ10 would significantly enhance its absorption.* It saves the body the trouble of having to break down the CoQ10 molecule as it is already delivered as a small particle. It would eliminate the need to take CoQ10 with a fatty meal to promote absorption. Similarly, this technology is a ground-breaking way to significantly enhance the bioavailability of a whole host of other nutrients.
Conclusions
A number of dietary supplements are plagued by poor bioavailability, limiting their clinical usefulness. A state-of-the-art delivery system that encapsulates nutrients within a whey protein matrix can significantly increase their absorption, antioxidant activity, and stability.* DaVinci Laboratories is excited to introduce Glutathione with Provail® and Glutathione Bright with Provail®, oral glutathione supplements that incorporate this scientifically proven and patented whey protein nutrient delivery system. The encapsulation technology promotes optimal bioavailability of GSH. Glutathione is protected inside of the ultra-small whey protein matrix, which acts like an envelope, preserving GSH in the GI tract and extending its shelf life. With this novel protective whey coating and a decreased particle size, GSH absorbs faster, increases blood levels, and reaches target tissues effectively.* Get better clinical results with Glutathione with Provail® and Glutathione Bright with Provail®. This technology is a monumental step forward for the dietary supplement industry, and in the future, DaVinci Laboratories is eager to extend its whey protein encapsulation offerings beyond glutathione to other difficult-to-absorb nutrients.
References:
- Krebs NF. Bioavailability of dietary supplements and impact of physiologic state: infants, children and adolescents. J Nutr. Apr 2001;131(4 Suppl):1351S-4S. doi:10.1093/jn/131.4.1351S
- Zhang S, Wang C, Zhong W, Kemp AH, Guo M, Killpartrick A. Polymerized Whey Protein Concentrate-Based Glutathione Delivery System: Physicochemical Characterization, Bioavailability and Sub-Chronic Toxicity Evaluation. Molecules. Mar 24 2021;26(7)doi:10.3390/molecules26071824
- Khan A, Wang C, Sun X, Killpartrick A, Guo M. Preparation and Characterization of Whey Protein Isolate-DIM Nanoparticles. Int J Mol Sci. Aug 12 2019;20(16)doi:10.3390/ijms20163917
- Herzenberg LA, De Rosa SC, Dubs JG, et al. Glutathione deficiency is associated with ... Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. Mar 4 1997;94(5):1967-72. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.5.1967
- Forman HJ, Zhang H, Rinna A. Glutathione: overview of its protective roles, measurement, and biosynthesis. Molecular aspects of medicine. Feb-Apr 2009;30(1-2):1-12. doi:10.1016/j.mam.2008.08.006
- Wu G, Fang YZ, Yang S, Lupton JR, Turner ND. Glutathione metabolism and its implications for health. J Nutr. Mar 2004;134(3):489-92. doi:10.1093/jn/134.3.489
- Maurice MM, Nakamura H, van der Voort EA, et al. Evidence for the role of an altered redox state in hyporesponsiveness of synovial T cells in ... J Immunol. Feb 1 1997;158(3):1458-65.
- Tretter L, Sipos I, Adam-Vizi V. Initiation of neuronal damage by complex I deficiency and oxidative stress in ... Neurochem Res. Mar 2004;29(3):569-77. doi:10.1023/b:nere.0000014827.94562.4b
- Witschi A, Reddy S, Stofer B, Lauterburg BH. The systemic availability of oral glutathione. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1992;43(6):667-9. doi:10.1007/bf02284971
- Allen J, Bradley RD. Effects of oral glutathione supplementation on systemic oxidative stress biomarkers in human volunteers. J Altern Complement Med. Sep 2011;17(9):827-33. doi:10.1089/acm.2010.0716
- Pizzorno J. Glutathione! Integr Med (Encinitas). Feb 2014;13(1):8-12.
- Richie JP, Jr., Nichenametla S, Neidig W, et al. Randomized controlled trial of oral glutathione supplementation on body stores of glutathione. Eur J Nutr. Mar 2015;54(2):251-63. doi:10.1007/s00394-014-0706-z
- Guo MR, Fox PF, Flynn A, Kindstedt PS. Susceptibility of beta-lactoglobulin and sodium caseinate to proteolysis by pepsin and trypsin. J Dairy Sci. Nov 1995;78(11):2336-44. doi:10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(95)76860-6
- Bounous G, Batist G, Gold P. Immunoenhancing property of dietary whey protein in mice: role of glutathione. Clin Invest Med. Jun 1989;12(3):154-61.
- Bounous G, Batist G, Gold P. Whey proteins in … prevention. Cancer Lett. May 1 1991;57(2):91-4. doi:10.1016/0304-3835(91)90200-2
- Unpublished Study. 2019.
- Weinbreck F, Minor M, de Kruif CG. Microencapsulation of oils using whey protein/gum Arabic coacervates. J Microencapsul. Sep 2004;21(6):667-79. doi:10.1080/02652040400008499
- Abbasi A, Emam-Djomeh Z, Mousavi MA, Davoodi D. Stability of vitamin D(3) encapsulated in nanoparticles of whey protein isolate. Food Chem. Jan 15 2014;143:379-83. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.08.018
- Shen X, Zhao C, Lu J, Guo M. Physicochemical Properties of Whey-Protein-Stabilized Astaxanthin Nanodispersion and Its Transport via a Caco-2 Monolayer. J Agric Food Chem. Feb 14 2018;66(6):1472-1478. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.7b05284
- Khem S, Small DM, May BK. The behaviour of whey protein isolate in protecting Lactobacillus plantarum. Food Chem. Jan 1 2016;190:717-723. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.06.020
- Liu K, Zha XQ, Shen WD, Li QM, Pan LH, Luo JP. The hydrogel of whey protein isolate coated by lotus root amylopectin enhance the stability and bioavailability of quercetin. Carbohydr Polym. May 15 2020;236:116009. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116009
- Jain A, Sharma G, Ghoshal G, et al. Lycopene loaded whey protein isolate nanoparticles: An innovative endeavor for enhanced bioavailability of lycopene and … activity. Int J Pharm. Jul 30 2018;546(1-2):97-105. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2018.04.061
- Walzem RL, Dillard CJ, German JB. Whey components: millennia of evolution create functionalities for mammalian nutrition: what we know and what we may be overlooking. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. Jul 2002;42(4):353-75. doi:10.1080/10408690290825574
- Cross ML, Gill HS. Immunomodulatory properties of milk. Br J Nutr. Nov 2000;84 Suppl 1:S81-9. doi:10.1017/s0007114500002294
- Tong LM, Sasaki S, McClements DJ, Decker EA. Mechanisms of the antioxidant activity of a high molecular weight fraction of whey. J Agric Food Chem. May 2000;48(5):1473-8. doi:10.1021/jf991342v
- Lefferts WK, Augustine JA, Spartano NL, et al. Effects of Whey Protein Supplementation on Aortic Stiffness, Cerebral Blood Flow, and Cognitive Function in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: Findings from the ANCHORS A-WHEY Clinical Trial. Nutrients. Apr 10 2020;12(4)doi:10.3390/nu12041054
- Cereda E, Turri A, Klersy C, et al. Whey protein isolate supplementation improves body composition, muscle strength, and treatment tolerance in malnourished advanced … patients undergoing .... Cancer Med. Nov 2019;8(16):6923-6932. doi:10.1002/cam4.2517
- Rondanelli M, Klersy C, Terracol G, et al. Whey protein, amino acids, and vitamin D supplementation with physical activity increases fat-free mass and strength, functionality, and quality of life and decreases inflammation in sarcopenic elderly. Am J Clin Nutr. Mar 2016;103(3):830-40. doi:10.3945/ajcn.115.113357
- Simoliunas E, Rinkunaite I, Bukelskiene Z, Bukelskiene V. Bioavailability of Different Vitamin D Oral Supplements in Laboratory Animal Model. Medicina (Kaunas). Jun 10 2019;55(6)doi:10.3390/medicina55060265
- Hernandez L. Microencapsulation and Nutritional Supplements. Accessed July 23, 2021. https://www.naturalproductsinsider.com/vitamins-minerals/microencapsulation-and-nutritional-supplements.
- Pravst I, Zmitek K, Zmitek J. Coenzyme Q10 contents in foods and fortification strategies. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. Apr 2010;50(4):269-80. doi:10.1080/10408390902773037
- Zaki NM. Strategies for oral delivery and mitochondrial targeting of CoQ10. Drug Deliv. Jul 2016;23(6):1868-81. doi:10.3109/10717544.2014.993747
